Steady-State vs. Transient Visual Evoked
Potential (VEP)
Ai-Hou Wang, M.D., Ph.D.
誘發電位是對感官給予刺激,記錄神經傳到大腦引發的電反應。視覺刺激引發的電位是視誘發電位(Visual
Evoked Potential,VEP),聽覺刺激引發的電位是聽誘發電位(Auditory
Brainstem Evoked Potential,ABEP),體表電刺激引發的電位是體誘發電位(Somatosensory Evoked
Potential,SSEP)。
Evoked potentials are electrical responses
recorded when sensory stimuli are applied and transmitted to the brain. Visual
evoked potentials (VEPs) are potentials elicited by visual stimuli, auditory
evoked potentials (ABEPs) are potentials elicited by auditory stimuli, and
somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs) are potentials elicited by electrical
stimulation of the body surface.
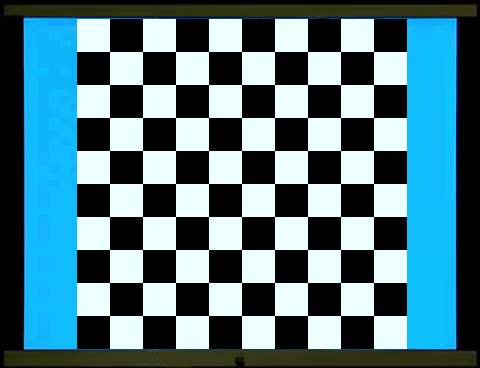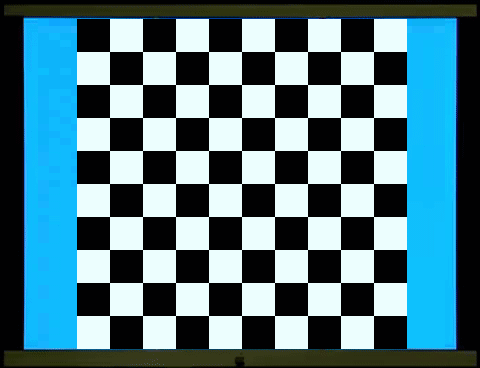
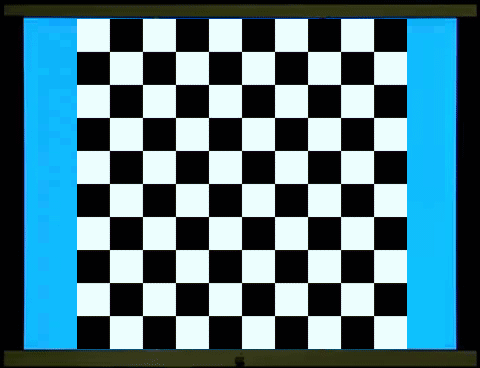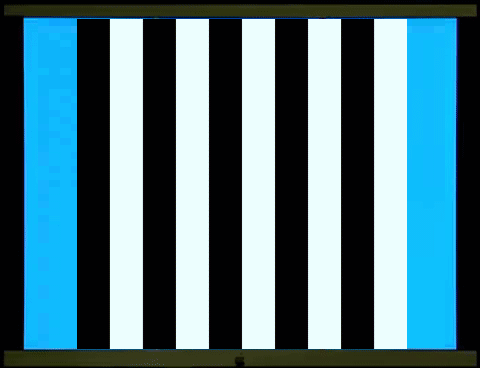
視覺刺激有閃光誘發電位(Flash
VEP)和圖像誘發電位(Pattern VEP)。臨床上通常使用圖像誘發電位,以西洋棋盤反轉(Checkerboard
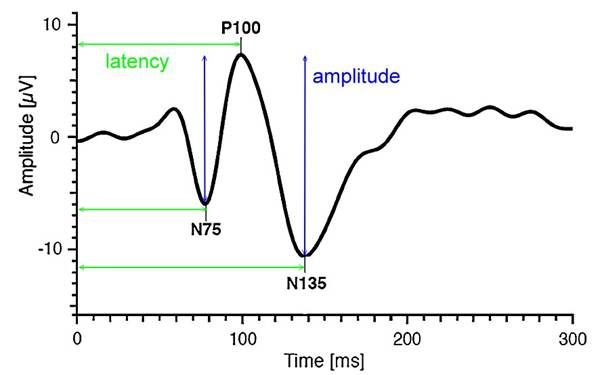
reversal)為視覺刺激,它的波形比閃光誘發電位穩定,重現性(Repeatability)高。典型的負正負(N75-P100-N135)波形(見圖),分析三個峰谷的潛期(latency)及兩個峰谷的電位幅度(amplitude)。和網膜電圖不同的是,波形的來源並沒有確切的神經、電位的分析
– 像網膜電圖的a波是光感細胞的過極化(hyperpolarization)電反應那樣,只能說是視路(optic pathway)上有些神經纖維傳導快、有些神經纖維傳導慢的綜合結果。
Visual stimuli include flash VEP and
pattern VEP. Clinically, pattern VEP is commonly used, with checkerboard
reversal as the visual stimulus. Its waveform is more stable and has higher
reproducibility than flash VEP. A typical negative-positive-negative
(N75-P100-N135) waveform (see figure) is analyzed, with the latency of the
three peaks and troughs and the amplitude of the potentials in the two peaks
and troughs. Unlike electroretinography, the source of the waveform is not
precisely analyzed for nerves or potentials – like the alpha wave in
electroretinography, which is a hyperpolarization electrical response of
photoreceptor cells, it can only be said to be a combined result of some nerve
fibers in the optic pathway conducting quickly and others slowly.
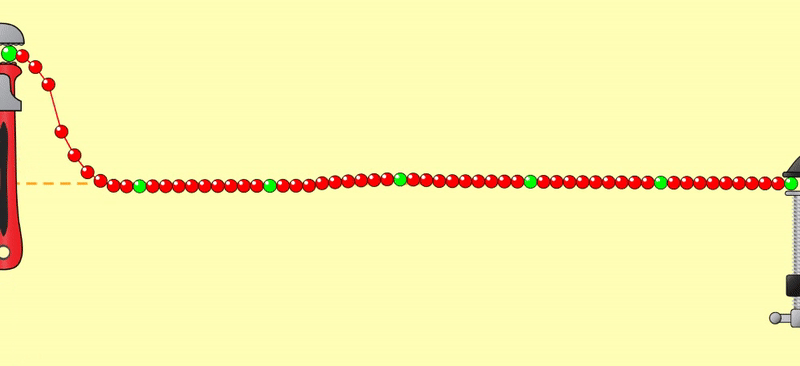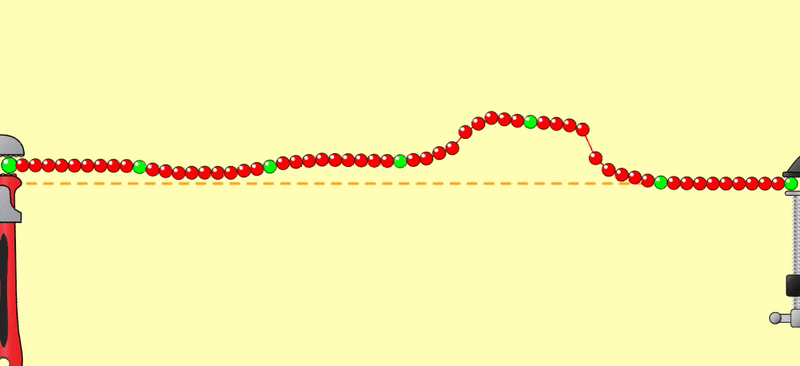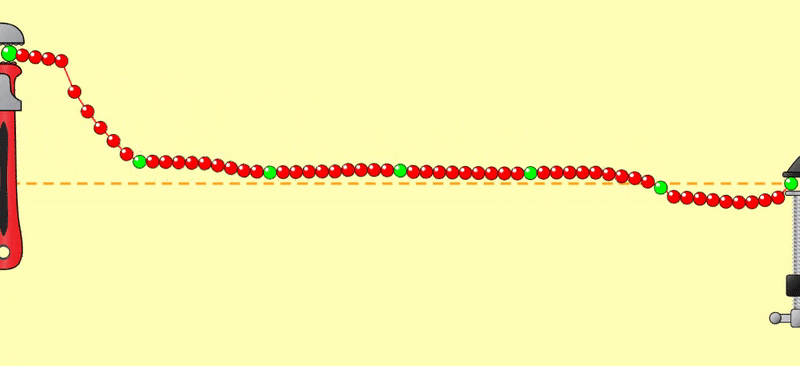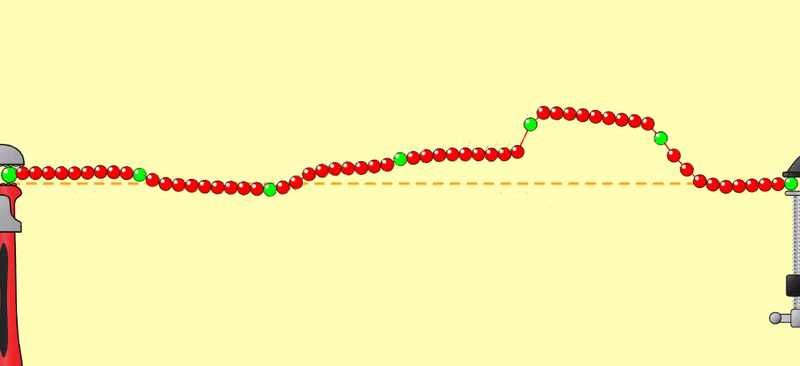
誘發電位可以比擬成甩繩(見圖),甩一下給予一個刺激,產生一個波形,好像視誘發電位的NPN波形(圖左)。甩快一點,一個波接著一個波(圖中),再快一點,前後波連到一塊兒(圖右),成了一個週期波。
Evoked
potentials can be likened to swinging a rope (see
figure). Each swing provides a stimulus and generates a waveform, similar to the NPN waveform of a visual evoked potential
(left figure). Swinging faster produces wave after wave (in the figure), and
even faster, the waves connect together (right
figure), forming a periodic wave.


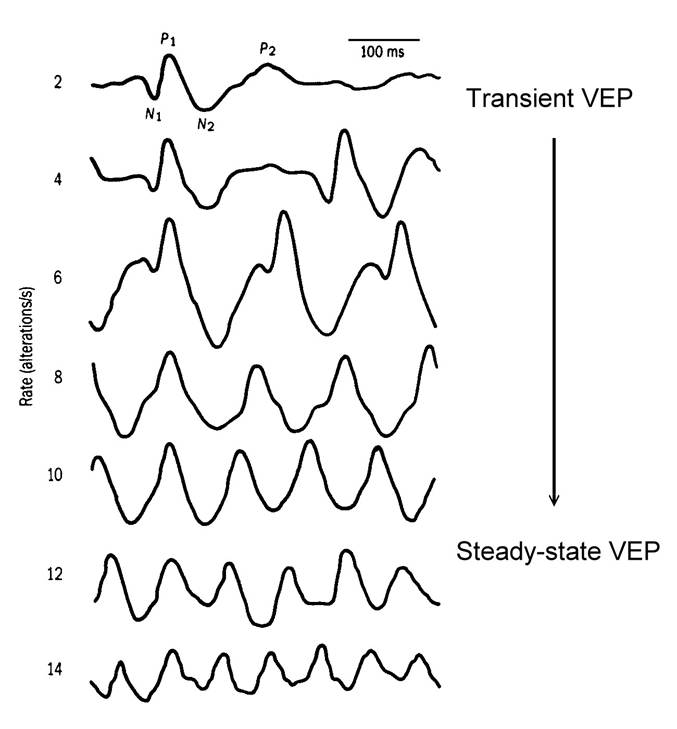
西洋棋盤反轉,每秒三、四個反轉得到個別的NPN波形,是暫態視誘發電位(Transient
VEP);每秒八個反轉以上,前後的NPN連在一塊兒,成為週期波,是穩態視誘發電位(Steady-state VEP)(見圖)。
When the chessboard is reversed, three or
four reversals per second produce individual NPN waveforms, which are transient
visual evoked potentials (VEPs). When there are more than eight reversals per
second, the preceding and following NPNs are connected
together to form a periodic wave, which is a steady-state visual evoked
potential (VEP) (see figure).
分析穩態視誘發電位的周期波使用傅立葉級數(Fourier
series),傅立葉級數說一個週期波可以分解成同頻率的正弦波和2倍頻率的正弦波和3倍頻率正弦波….和整數倍頻率的正弦波的和(1f+2f+3f+…..+nf+…..),級數收斂,加總的和漸漸趨近原始的週期波。每一個倍頻所占份量決定於該倍頻的振幅(amplitude)和相位(phase)。而基頻(f)就是視覺刺激輸入的頻率。
簡言之,暫態視誘發電位分析峰谷幅度和潛期,穩態視誘發電位分析各倍頻的振幅和相位。
暫態視誘發電位幅度低判讀為傳導的神經纖維少;潛期長判讀為神經傳遞慢。
穩態視誘發電位如果刺激圖像的西洋棋盤格子逐漸變小,相位會依次逐漸改變。
The periodic waves of steady-state visual
evoked potentials (PVPs) are analyzed using Fourier series. A Fourier series
states that a periodic wave can be decomposed into a sum of sine waves of the
same frequency, sine waves at twice the frequency, sine waves at three times
the frequency, and so on, up to integer multiples of the frequency (1f + 2f +
3f + ... + nf + ...). The series converges, and the
sum gradually approaches the original periodic wave. The proportion of each
harmonic is determined by its amplitude and phase. The fundamental frequency
(f) is the frequency of the visual stimulus input.
In short, transient visual
evoked potentials analyze peak and trough amplitudes and latency, while
steady-state visual evoked potentials analyze the amplitude and phase of
each harmonic.
A low amplitude in transient visual evoked
potentials indicates fewer nerve fibers conducting the
signal; a long latency indicates slow nerve transmission.
In steady-state visual evoked potentials,
if the checkerboard grid of the stimulus image gradually decreases in size, the
phase will gradually change accordingly.
這裡列舉四個穩態視誘發電位的臨床和視覺科研的應用
1. 嬰幼兒視皮質盲的視誘發電位
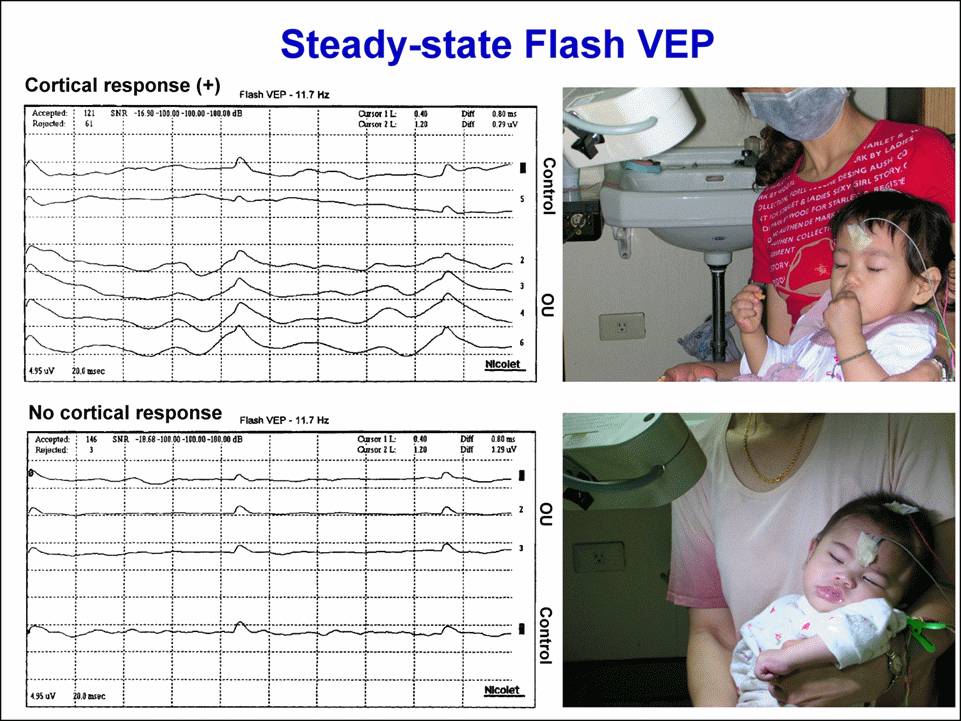
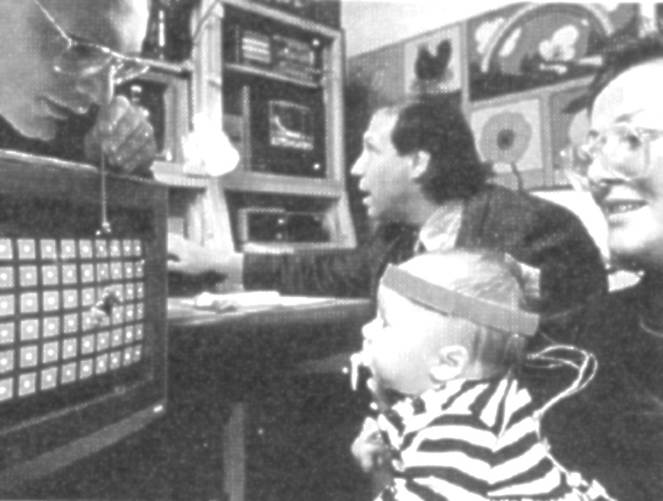
嬰幼兒注意力差、不會注視。對那些反應差,門診檢查無法判斷他看不看得見的嬰幼兒,眼科醫師會想作視誘發電位來判斷。一般使用的西洋棋盤圖像視誘發電位,受試者必須專心注視螢幕,這些小兒通常無法注視,得到的誘發電位波形常常不是典型的NPN波形,哪兒是NPN的波峰、波谷不容易決定,波幅和潛期也就沒法判讀,也就沒法判斷小兒是否仍有視力。
在這種情況,我們建議作閃光穩態視誘發電位。我們用11.7Hz(避開整數12Hz,避開交流電干擾)的強閃光,小兒閉著眼也可以接受到閃光。媽媽抱著,沒有麻醉、鎮靜。對照組是將閃光燈用黑布套包起來,一樣在布套裡閃光,排除閃光燈放出強電場造成的假象誘發電位。記錄是1/5秒、200msec,有2.3+週誘發電位(見圖)。上圖判讀為對強光有視誘發電位:下圖判讀為對強光沒有視誘發電位。
嬰幼兒的視誘發電位是隨著年齡長大漸漸發展出來的。有視誘發電位可以判讀為至少有光覺(light
perception);沒有視誘發電位卻不一定代表沒有視力,通常幾個月後重作視誘發電位檢查,再評估一次。視力是後天發育的,以視誘發電位估計視力有很大的侷限性。相對地,耳鼻喉科居然可以對嬰兒用聽誘發電位篩檢聽力的有無和好壞!主要的原因是聽力在肚子裡已經大致發育完整,許多孕婦會隔著肚皮跟胎兒講話,隔著肚皮放音樂胎教。這和嬰幼兒的視力評估是非常不一樣的。
Here are four applications of steady-state
visual evoked potentials (SVPs) in clinical and visual research:
1. Visual Evoked Potentials in Infants
with Cortical Visual Impairment
Infants often have poor attention spans
and cannot fixate. For infants with poor responsiveness, where outpatient
examinations cannot determine their visual acuity, ophthalmologists may perform
SVPs to assess this. Commonly used checkerboard image SVPs require subjects to
focus intently on a screen, which these children typically cannot achieve. The
resulting evoked potential waveforms are often not typical NPN waveforms;
identifying the peaks and troughs of the NPN is difficult, making it impossible
to determine the amplitude and latency, and consequently, whether the child
still has vision.
In such cases, we recommend using flash
steady-state visual evoked potentials. We use a strong flash at 11.7 Hz
(avoiding integers like 12 Hz to prevent AC interference), which the child can
perceive even with their eyes closed. The child is held by their mother without
anesthesia or sedation. The control group had the flash lamp wrapped in a black
cloth cover and flashed inside the cover, eliminating the possibility of
spurious evoked potentials caused by the strong electric field emitted by the
flash lamp. The recording time was 1/5 second, 200 msec, with 2.3+ weeks of
evoked potentials (see figure). The top figure is interpreted as having visual
evoked potentials in response to bright light; the
bottom figure is interpreted as not having visual evoked potentials
in response to bright light.
Visual evoked potentials
in infants and young children develop gradually with age. The presence of
visual evoked potentials indicates at least light
perception; the absence of visual evoked potentials
does not necessarily mean the absence of vision. Usually, a repeat visual
evoked potential test is performed after several months for reassessment.
Vision is developed after birth, and estimating vision using visual evoked potentials has significant limitations. In contrast, ENT
specialists can even use auditory evoked potentials to screen for the presence
and quality of hearing in infants! The main reason is that hearing is largely
developed in the womb, and many pregnant women talk to their fetuses through
their bellies or play music for prenatal education. This is very different from
assessing vision in infants and young children.
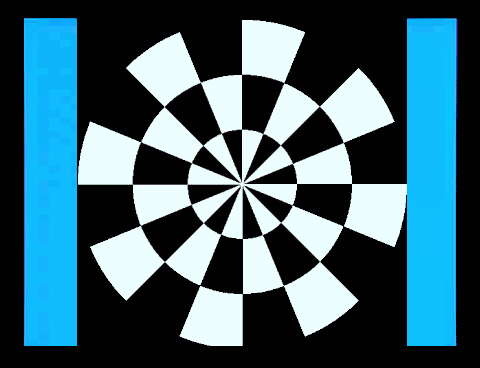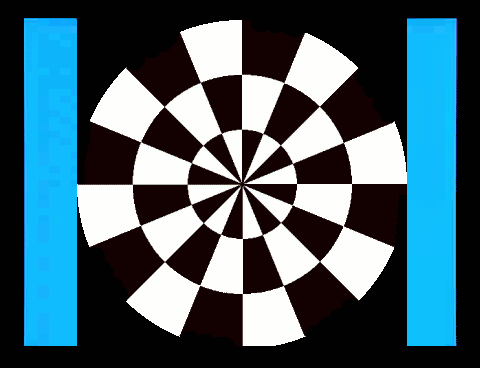
2. 鏢靶(Dartboard)
/ 風車(Windmill) 反轉 視誘發電位
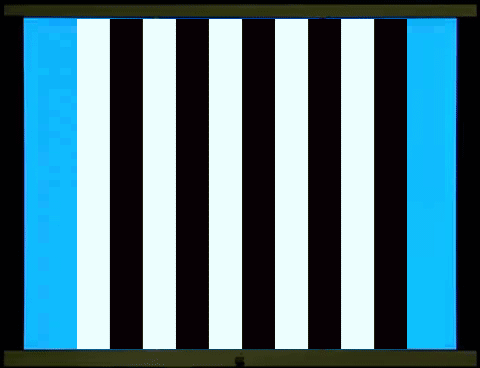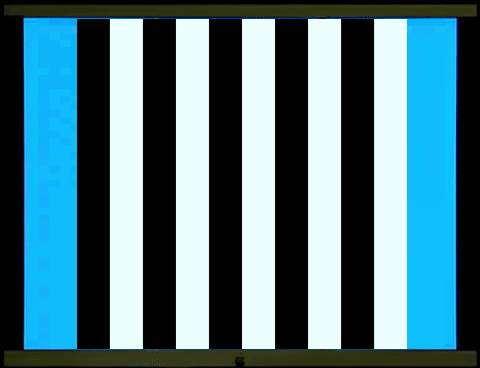
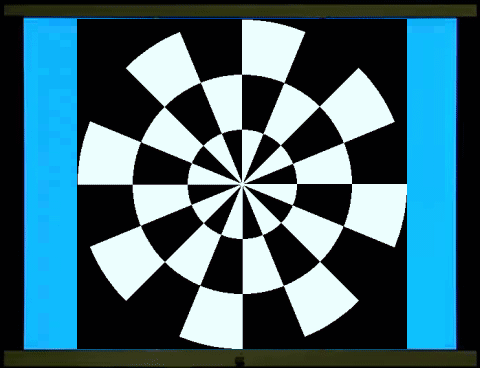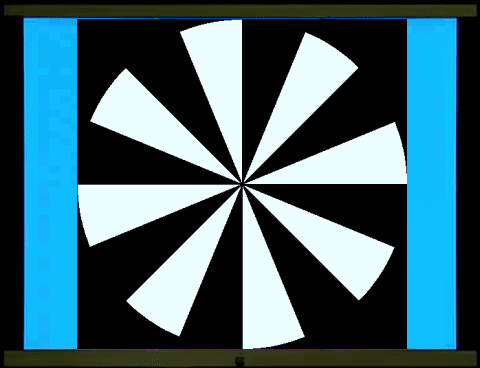
西洋棋盤反轉是西洋棋盤1和西洋棋盤2交替展現。棋盤1、2各出現一次是一個週期(cycle),一個週期是兩個反轉(reversal),每秒6週(Hz)也就是12反轉。棋盤1轉到棋盤2和棋盤2轉到棋盤1,在一般人的知覺、認知上覺得是一樣的,你可以數得出反轉,卻不容易數得出週期。這裡穩態視誘發電位2倍頻率(2f,反轉)的波幅遠大於基頻(1f,週期)的波幅(左圖)。
西洋棋盤是半黑半白的圖像,柵紋(Grating)也是半黑半白的圖像。棋盤、柵紋交替展現,螢幕的平均亮度維持不變(中圖),沒有亮度變化誘發的電位,符合圖像視刺激的基本要求。但是主觀的知覺上,棋盤轉到柵紋和柵紋轉到棋盤感覺就不一樣,可以很容易數得出週期。同樣6週、12反轉的圖像刺激,穩態視誘發電位在2倍頻率(2f,反轉)的波幅變小,基頻(1f,週期)的波幅變大。
右圖是柵紋反轉,如同西洋棋盤反轉,穩態視誘發電位在2倍頻率(
2. Dartboard/Windmill Reversal Visual
Evoked Potentials
The chessboard reversal involves
alternating displays of chessboard 1 and chessboard 2. One appearance of each
chessboard constitutes one cycle, and one cycle consists of two reversals,
occurring at 6 cycles per second (Hz), or 12 reversals. The rotation of
chessboard 1 to chessboard 2 and vice versa is perceived as identical to most
people; you can count the reversals, but not necessarily the cycle. Here, the
amplitude of the steady-state visual evoked potential at twice the frequency
(2f, reversal) is much larger than the amplitude of the fundamental frequency
(1f, cycle) (left image).
The chessboard is
a half-black, half-white image, and the grating is also a half-black,
half-white image. The chessboard and grating are displayed alternately, while
the average brightness of the screen remains constant (middle image), without
any brightness-induced potentials, meeting the basic
requirements of visual stimulation. However, subjectively, the feeling of the
chessboard turning to the grating and the grating turning to the chessboard is
different, and the cycle can be easily counted. For the same 6-cycle,
12-reversal image stimulus, the amplitude of the steady-state visual evoked
potential at twice the frequency (2f, reversal) decreases, while the amplitude
at the fundamental frequency (1f, cycle) increases.
The right image shows grating reversal, similar to the reversal of a chessboard; the amplitude of
the steady-state visual evoked potential at twice the frequency (2f) is much
greater than the amplitude at the fundamental frequency (1f).
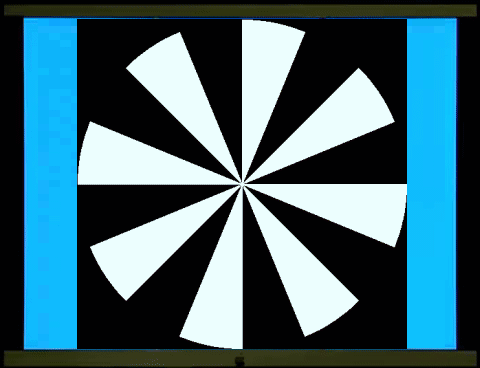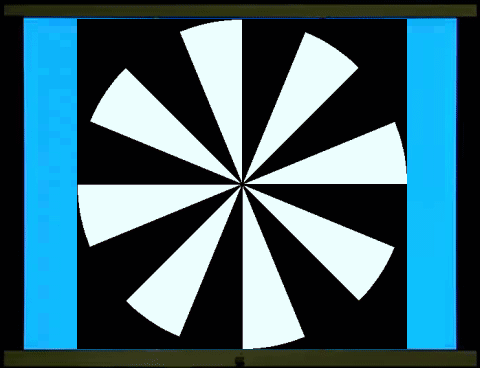
鏢靶、風車交替展現和西洋棋盤、柵紋交替展現的圖像視誘發電位非常類似,只是前者更符合視野中央、週邊的分布。鏢靶/鏢靶反轉(左圖)和風車/風車反轉(右圖)的視誘發電位的能量會聚集在2倍頻率(
The visual evoked potentials (VAPs) of
alternating dartboard and windmill images are very similar to those of
alternating chessboard and grid patterns, except that the former better matches
the distribution of the center and periphery of the field of vision. The energy
of the VAPs of dartboard/dartboard reversal (left image) and
windmill/windmill reversal (right image) is
concentrated at twice the frequency (2f), while the VAP of dartboard/windmill
(middle image) has more energy at the fundamental frequency (1f).
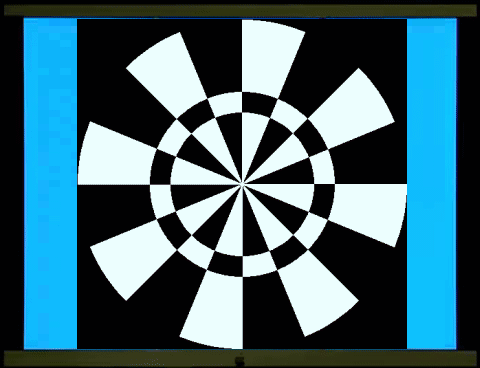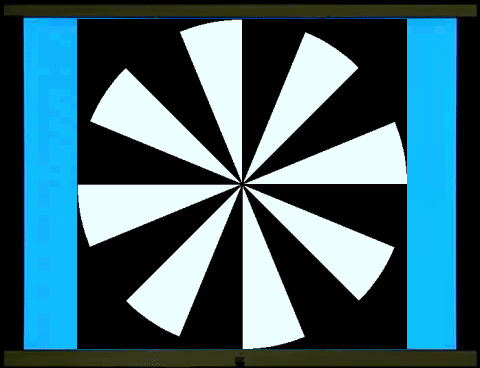
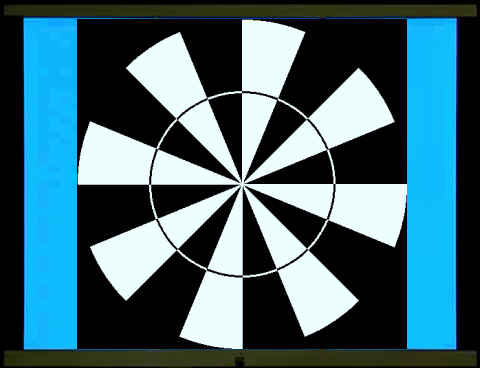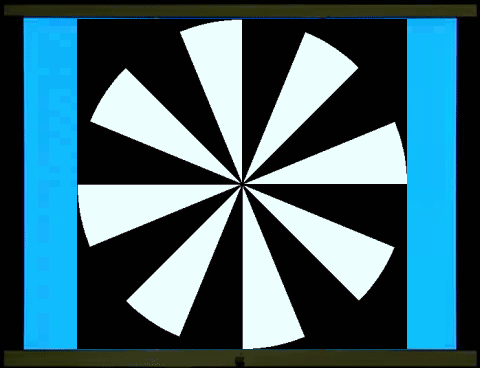
三環的鏢靶/風車反轉,當中間的一環寬的時候(左圖),視誘發電位集中在基頻(
將中間的一環置於不同的周邊位置(periphery),可以探測不同周邊網膜處側向細胞側向連結的長度的改變。
In the three-ring dartboard/windmill
reversal pattern, when the middle ring is wide (left image), visual evoked
potentials (VEPs) are concentrated at the fundamental frequency (1f). As the
middle ring gradually narrows (middle image) and becomes even narrower,
gradually reverting to a windmill/windmill reversal (right image), the VEPs
shift to a two-fold frequency (2f). The change in the input, the width of the
middle ring, affects the length of the lateral connections of lateral cells on
the retina – including horizontal cells and amacrine cells; the output is a
shift in the predominance of the fundamental frequency (1f) to the two-fold
frequency (2f) in the evoked potentials perceived by the visual cortex.
By placing the middle ring in different
peripheral locations, changes in the length of the lateral connections of
lateral cells in different peripheral retina locations can be detected.

3. 立體視的視誘發電位(Visual
Evoked Potential,VEP
of Stereopsis) – 動態隨機點立體圖(Dynamic
Random-dot Stereogram)
下圖是設計來記錄立體視的視誘發電位的圖形,共16張隱藏西洋棋盤的立體圖,其中8張包含左上角那格凸起的西洋棋盤,另8張包含左上角那格凹下的西洋棋盤,反覆播放,就如同一般臨床上視誘發電位檢查使用的西洋棋盤反轉圖樣。電腦螢幕每秒展示60張畫面,每一個畫面變換1張立體圖,16張立體圖是一個週期(Cycle),一個週期西洋棋盤反轉(Reversal)2次,基頻(
這裡的西洋棋盤不是黑白反轉,而是深度的反轉。左眼、右眼單眼所見的圖樣,看起來好像是電視收播之後的雪暴圖(Snow storm),雙眼一起看,所見到的西洋棋盤以7.5反轉/秒的頻率作深度反轉,視誘發電位如果記錄到這個頻率的電位信號,它必定是大腦被立體視所誘發的反應,因為左右眼單眼各自都不存在這個頻率的信號輸入。
3. Visual Evoked Potential (VEP) of Stereopsis – Dynamic Random-dot Stereogram
The image below shows a pattern designed to record visual evoked potentials (VEPs) of stereopsis. It consists of 16
stereoscopic images of a hidden chessboard. Eight images include the raised
square in the upper left corner, and the other eight include the recessed
square. These are played repeatedly, similar to the
reversed chessboard patterns used in clinical VEP examinations. The computer
screen displays 60 frames per second, with each frame displaying one
stereoscopic image. The 16 images constitute one cycle. The chessboard reverses
twice per cycle. The fundamental frequency (1f) is 60/16 = 3.75 Hz, and the
second harmonic frequency (2f) is 7.5 reversals per second. A signal of 7.5
reversals per second extracted from the brainwaves represents the stereoscopic
evoked potential.
The chessboard here isn't a black-and-white inversion, but a depth
inversion. The pattern seen by the left and right eyes looks like a snowstorm
image after a television broadcast. When viewed with both eyes, the chessboard
appears to undergo a depth inversion at a frequency of 7.5 inversions per
second. If visual evoked potentials record a potential signal at this
frequency, it must be a response of the brain induced by stereopsis, because
neither eye individually receives a signal input at this frequency.

這張圖就是所謂的動態隨機點立體圖,深度覺是來自於每一張圖裡左右眼的像差(disparity)。它不是運動立體圖,每一張立體圖的背景和前景都不一樣,並不包含有運動覺(motion perception)的視覺刺激。
This image is a so-called dynamic random
dot stereogram. Depth perception comes from the disparity between the left and
right eyes in each image. It is not a motion stereogram; the background and
foreground of each stereogram are different, and it does not contain visual
stimuli for motion perception.
Norcia AM. Frequency
Domain Analysis of Human Stereopsis. Thesis, Stanford University
4. 運動覺(Motion
perception) / 視動眼震(Optokinetice
nystagmus,OKN) 鼻顳側不對稱(Naso-temporal
asymmetry) 視誘發電位
嬰幼兒單眼的視動眼震是鼻、顳側不對稱的。所見景像由顳側向鼻側移動,會誘發快速相朝向顳側的視動眼震;而景像由鼻側向顳側移動,則不會誘發快速相朝向鼻側的視動眼震。也就是右眼偏好向左移動的景象,產生快速相向右的視動眼震,但是對於向右移動的景象,卻不會產生快速相向左的視動眼震;左眼相反過來,偏好向右移動的景象,產生快速相向左的視動眼震,但是對於向左移動的景象,卻不會產生快速相向右的視動眼震。
Dr. Anthony Norcia(見圖)以穩態視誘發電位記錄運動覺鼻、顳側的不對稱。
4. Motion
perception / Optokinetic nystagmus (OKN) Naso-temporal asymmetry Visual evoked
potentials
In infants and
young children, unilateral optokinetic nystagmus is asymmetrical between the
nasal and temporal sides. When an image moves from the temporal side to the
nasal side, it induces a fast-phase optokinetic nystagmus towards the temporal
side; conversely, when the image moves from the nasal side to the temporal
side, it does not induce a fast-phase optokinetic nystagmus towards the nasal
side. That is, the right eye prefers images moving to the left, producing a
fast-phase optokinetic nystagmus towards the right, but not for images moving
to the right, producing a fast-phase optokinetic nystagmus towards the left;
the left eye is the opposite, preferring images moving to the right, producing
a fast-phase optokinetic nystagmus towards the left, but not for images moving
to the left, producing a fast-phase optokinetic nystagmus towards the right.
Dr. Anthony
Norcia (see figure) used steady-state visual evoked potentials to record the
asymmetry of motor perception on the nasal and temporal sides.


視刺激器是兩張正弦柵紋 – 左右岔開1/4空間週期
– 交替展現。一黑一白條紋是一個空間週期,或稱為360°,兩張柵紋則是岔開90°,左右搖擺、振動著(jittering)(見圖)。
The visual stimulator consists of two
sinusoidal gratings – spaced 1/4 of a spatial cycle apart – that alternate. One
black and one white stripe represent one spatial cycle, or 360°, while the two
gratings are spaced 90° apart, swaying and jittering (see figure).

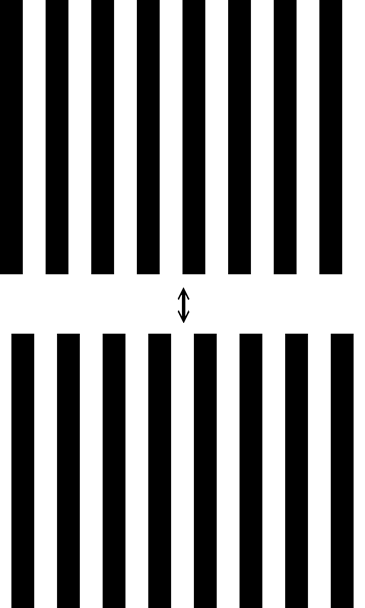
嬰幼兒單眼的運動覺是鼻、顳側不對稱的。正常的成長過程,這不對稱在半歲到一歲漸漸發育成為鼻、顳側對稱的。幼兒型內斜視(Infantile esotropia)的病人即便長大成人,運動覺依舊維持是鼻、顳側不對稱的。
運動覺鼻、顳側不對稱的人,右眼偏好向左的運動,左眼偏好向右的運動。柵紋左右搖擺,對右眼來說,向左運動誘發比較大的電位,向右運動誘發比較小的電位(上圖);對左眼來說,向右運動誘發比較大的電位,向左運動誘發比較小的電位(下圖)。穩態視誘發電位都有強的基頻(
In infants and young children, the
kinesthetic sense in one eye is asymmetrical between the nasal and temporal
sides. During normal development, this asymmetry gradually develops into
symmetrical kinesthetic sense between six months and one year of age. Even in
adulthood, patients with infantile esotropia retain this asymmetry between the
nasal and temporal sides of their kinesthetic sense.
In individuals with asymmetrical
kinesthetic sense between the nasal and temporal sides, the right eye prefers
leftward movement, and the left eye prefers rightward movement. When the
lattice fringes oscillate from side to side, for the right eye, leftward
movement evokes a larger potential, and rightward movement evokes a smaller
potential (top image); for the left eye, rightward movement evokes a larger
potential, and leftward movement evokes a smaller potential (bottom image).
Steady-state visual evoked potentials all have a strong fundamental frequency
(1f) potential, but the phases of the left and right eyes are separated by
180°.
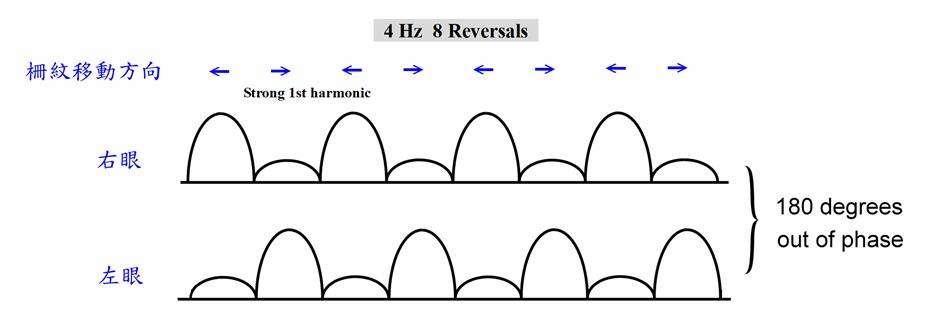
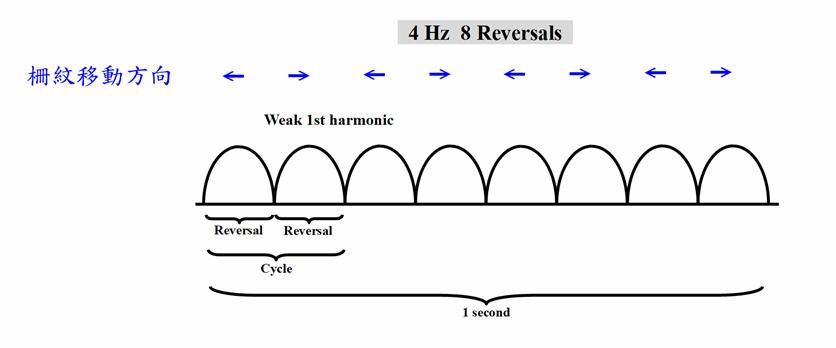
運動覺鼻、顳側對稱的人,向左運動和向右運動誘發相同的電位,穩態視誘發電位於是集中在2倍頻率(
In individuals with symmetrical nasal and
temporal motor sensation, movement to the left and right evoked the same
potential, and the steady-state visual evoked potential was concentrated at
twice the frequency (2f) (see figure).
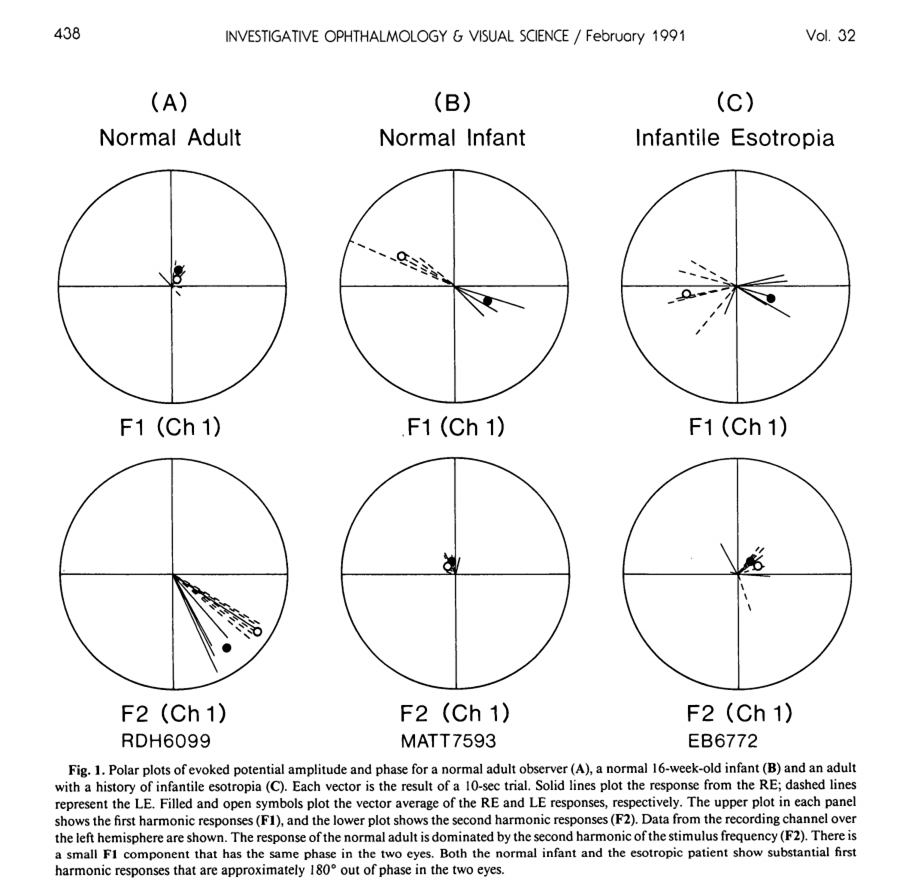
以極座標作圖,左圖(A)欄是正常成人,運動覺鼻、顳側是對稱的,穩態視誘發電位於是集中在2倍頻率(
Plotting using polar coordinates, the left
image (A) represents a normal adult. The motor senses of the nose and temporal
sides are symmetrical. Steady-state visual evoked signals are concentrated at
twice the frequency (2f), with very low energy at the fundamental frequency
(1f), and the phase difference between the two eyes is also the same. The
middle image (B) represents a normal infant. The motor senses of the nose and
temporal sides are asymmetrical. Steady-state visual evoked signals are
concentrated at the fundamental frequency (1f), with very low energy at twice
the frequency (2f), and the phase difference between the two eyes at the
fundamental frequency is 180°. The right image (C) represents an adult who grew
up with infantile esotropia. The motor senses of the nose and temporal sides
remain asymmetrical. Steady-state visual evoked signals are concentrated at the
fundamental frequency (1f), with very low energy at twice the frequency (2f),
and the phase difference between the two eyes at the fundamental frequency is
180°.
Norcia AM, Garcia H, Humphry R, Holmes A,
運動覺鼻、顳側不對稱表現在眼球的運動方面,有視動眼震鼻、顳側不對稱,反轉柵紋測試(Reversing grating test)鼻、顳側不對稱等等。這個不對稱的性質是存在視覺的感覺系統(sensory system)或運動系統(motor system)呢?從枕部電極的視誘發電位記錄,我們可以知道運動覺鼻、顳側不對稱性在感覺系統、視皮質就已經存在。
The asymmetry of the nasal and temporal
sides in kinesthetic perception manifests in eye movements, such as nasal and
temporal asymmetry in optomotor nystagmus and the reversing grating test. Is
this asymmetry present in the visual sensory system or the motor system? Visual
evoked potential records from occipital electrodes indicate that the nasal and
temporal asymmetry of kinesthetic perception already exists in the sensory
system and visual cortex.
Wang AH, Norcia AM, Jampolsky A. Reversing grating as a simple
clinical method to test the symmetry of motion perception and potential
binocularity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1993;33(4):1340.
隨著正常雙眼視的發育,鼻、顳側不對稱的運動覺漸漸發育成為鼻、顳側對稱的運動覺。越細的柵紋(高空間頻率)(右邊兩圖)、左右振動越快的柵紋(高時間頻率)(下面兩圖)發育成熟,或者說穩態視誘發電位由基頻(
As normal binocular vision
develops, asymmetrical nasal and temporal motor senses gradually develop into
symmetrical nasal and temporal motor senses. The finer the grating (higher
spatial frequency) (right two images) and the faster the lateral vibration of
the grating (higher temporal frequency) (bottom two images), the later the
steady-state visual evoked potentials develop from being predominantly at the
fundamental frequency (1f) to being predominantly at twice the frequency (2f).
Even in late-onset esotropia that occurs after age
two, visual evoked potentials can still record some nasal and temporal
asymmetry in motor senses.




Hamer RD, Norcia AM, Orel-Bixler D, Hoyt CS. Motion VEPs in late-onset esotropia. Clinical
vision sciences 1993;8(1):55-62.
及早手術或注射肉毒桿菌素(Botox)矯正幼兒型內斜視的眼位可以恢復週邊視野的融像功能(peripheral fusion),它是不是也可以促使鼻、顳側不對稱的運動覺發育成為鼻、顳側對稱的運動覺呢?Dr. Arthur Jampolsky、Dr. Keith
McNeer、Dr. Lawrence
Tychsen都曾經使用穩態視誘發電位證明那是可能的。
Early surgery
or injection of botulinum toxin to correct eye position in infantile esotropia
can restore peripheral fusion. Could it also promote the development of
asymmetrical nasal and temporal motor senses into symmetrical nasal and
temporal motor senses? Dr. Arthur Jampolsky, Dr. Keith McNeer, and Dr. Lawrence
Tychsen have all used steady-state visual evoked potentials to prove that this
is possible.



Dr. Arthur Jampolsky
Dr.
Keith McNeer Dr. Lawrence
Tychsen
Norcia AM, Jampolsky
A,
Norcia AM, McNeer K, Tucker M, Williams SM,
Hamer RD. Development of binocular motion
processing following oculinum injection in infantile esotropia.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992;33(4):870-870.
Tychsen L, Wong AM, Foeller P, Bradley D. Early versus delayed repair of infantile strabismus in macaque monkeys:
II. Effects on motion visually evoked responses. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 2004 Mar;45(3):821-7.
這套視誘發電位(VEP)的系統是Dr. Christopher Tyler和Dr. Anthony Norcia所開發,基本上是一種穩態(Steady-state)的視誘發電位。如果視刺激器的參數漸次改變,就成為掃掠視誘發電位(Sweep VEP),常作為評估小兒視覺發育的指標,掃掠的參數有大小(size,視力)、對比(contrast,對比敏感度)、運動(motion)、游標視力(vernier
acuity)等等。
This system of visual evoked potentials
(VEPs) was developed by Dr. Christopher Tyler and Dr. Anthony Norcia. It is
essentially a steady-state VEP. If the parameters of the visual stimulator are
gradually changed, it becomes a sweep VEP, often used as an indicator to assess
children's visual development. The sweep parameters include size (visual
acuity), contrast (contrast sensitivity), motion, vernier acuity, etc.


Dr. Anthony Norcia Dr. Christopher Tyler
使用這個VEP系統做視覺和眼科學研究的還有Dr. Eileen
Birch,Dr. Anne Fulton,Dr.
Agnes Wong等等。
Dr. Eileen Birch, Dr. Anne Fulton, Dr. Agnes Wong, and others have
also used this VEP system for vision and ophthalmology research.



Dr. Eileen
Birch
Dr. Anne Fulton Dr. Agnes Wong
附記 – 數位傅立葉分析 (Digital Fourier Analysis)
附上簡短的BASIC語言程式:
橫軸h個點
抽取m倍頻(mth harmonic)
[非快速傅立葉傳換(Fast Fourier Transform, FFT)]
Postscript – Digital Fourier
Analysis
A short BASIC program is
attached: Horizontal axis: h points Decimate by m harmonics
[Non-Fast Fourier Transform
(FFT)]
real = 0: imag = 0
FOR i
= 0 TO h - 1
real
= real + y(i) * COS(2 * pi * i
* m / h)
imag = imag + y(i) * SIN(2 * pi * i * m / h)
NEXT
amp = (real ^ 2 + imag ^ 2) ^ .5 / h * 2
IF real = 0 AND imag > 0 THEN
phase = .5 * pi
ELSEIF real = 0 AND imag < 0 THEN
phase = 1.5 * pi
ELSE
phase =
ATN(imag / real)
IF
real < 0 THEN phase = phase + pi
IF
real > 0 AND imag < 0 THEN phase = phase + 2 *
pi
END IF
IF phase >= 2 * pi THEN
phase = phase - 2 * pi
phase = phase / pi