About
NTU300
National
Taiwan University Random-dot Stereograms (NTU RDS) 300 sec-of-arc
A
popular tool for visual screening of pre-school and school children in Taiwan
Ai-Hou
Wang, M.D., Ph.D.
Dr.
Song-Yang Wei asked me about the origins of NTU300, so here’s a review.
The
random-dot stereogram (RDS) was invented in 1960 by Dr. Bela Julesz at Bell Labs. It is an invention, not a discovery,
because RDS did not exist in the universe before.
Another
"invention" in 1960 was the ruby laser. There was no laser light in
the universe; Einstein predicted the possibility of coherent light, which led
to the emergence of the first physical laser in 1960.
In
1982, during my ophthalmology residency, Dr. Luke L-K Lin used Titmus and TNO
for stereopsis tests. Titmus belongs to contour stereograms, the 3D images
(like a fly) are visible to one eye; TNO, on the other hand, is a random-dot
stereogram, where the hidden image (like a butterfly) cannot be seen with
either eye. Small angle esotropia and anisometropia may not be detected through
the Titmus test, but they are impossible to pass TNO Stereotest.
Clinically,
the most criticized aspect of using random-dot stereograms to test stereopsis
is that everyday environments do not resemble the scenarios presented by
random-dot patterns. At most, one might encounter some similar situation while
searching for a small bird or a cicada in the bushes. However, after a period
of clinical experience, we have learned that random-dot stereopsis tests are
indeed a useful tool for diagnosing and screening strabismus and amblyopia.
The
mechanisms of stereopsis in contour stereograms and random-dot stereograms are
different: in contour stereopsis, such as Titmus, the right eye sees a fly and
the left eye also sees a fly. The brain recognizes that the flies in the two
eyes fall at different coordinates, there exists a disparity, which is
converted into depth perception, resulting in a 3D sensation. In random-dot
stereopsis, such as TNO, neither the right eye nor the left eye sees a
butterfly initially; after the images from both eyes fuse together, the
butterfly emerges. But what are the two eyes fusing? The only possibility is
the fusion of random-dot textures. After the random-dot textures from both eyes
are combined, the brain detects the hidden disparity and then decodes the
butterfly.
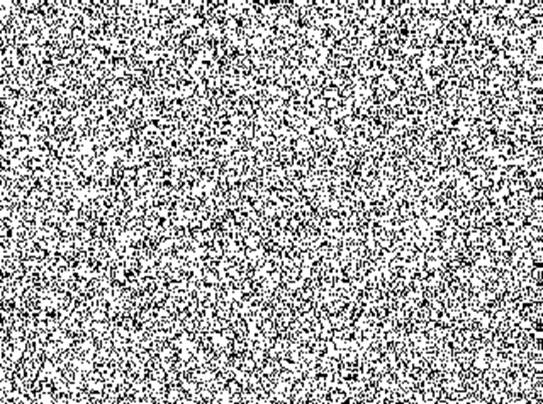
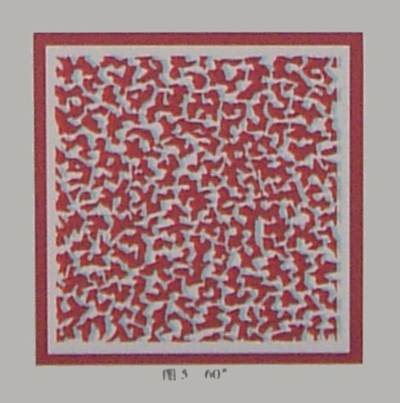
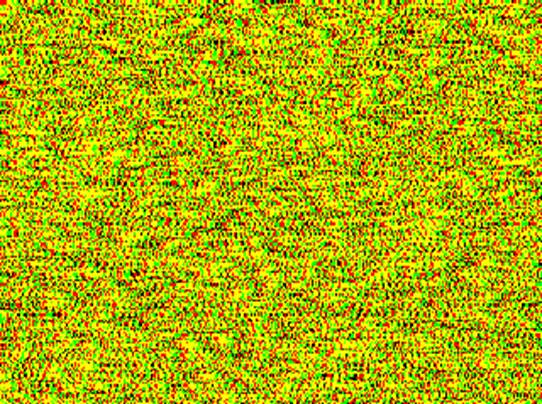
This
is a random-dot pattern used in NTU300, consisting of 320x240 pixels (picture
elements) with 50% density. The so-called texture refers to the patterns formed
by the clustering of black dots in some areas and white dots in others.
I
was very interested in creating my own random-dot stereograms. At that time,
the personal computer I used was Apple II. I utilized several existing software
tools, relying on graphic shifts and logical operations between two images
(AND, OR, NOT, XOR). I prepared two random-dot images at 50% density, one for
the foreground and one for the background, along with a black-and-white image
that I wanted to embed into the random-dot stereogram. I designed a
step-by-step process that allowed me to create a random-dot stereogram with
those three elements.
This
process was presented at the 1986 ISA (International Strabismological
Association) conference in Rome – "Random-dot stereogram made with
personal computer - ISA V Rome 1986."
Here
is a step-by-step process for creating random-dot stereograms that you can
refer to:
https://ahwang.url.tw/WebArticles/Creating%20RDS%20step-by-step-English.htm.
The
program prepares two random-dot patterns at 50% density and one black-and-white
figure to be embedded. The program can automatically generate a random-dot
stereogram that conceals this figure.
Creating
Random-dot Stereogram: Step-by-Step.ppt
(Powerpoint file. It cannot be played on
Google Drive. Please download and play on your computer.)
Creating
Random-dot Stereogram: Step-by-Step.exe
(You may need to temporarily
disable "Real-time Scan" in your antivirus software.)
The
Apple II had a very slow operating speed, and the resolution of the graphics
was low, with a width of only 320 pixels. The minimum disparity between the
left and right eye half-stereograms in a random-dot stereogram is one pixel. If
displayed on a 15-inch screen, the width is 12 inches (1 foot) (30.48 cm) and the height is 9 inches. This means that the horizontal
span of 320 pixels corresponds to 30.48 cm. Using the formula
30.48/320/distance x 180/pi x 60 x 60 = 300”, we calculate that if the visual
angle of a pixel is 300 sec-of-arc (or 5 min-of-arc), the test distance should
be 65 cm.
If
printed on a 4x6 inch photo, the width is 6 inches (15.24 cm)
and the height is 4 inches. The horizontal span of 320 pixels corresponds to
15.24 cm. Using the same calculation, at a test distance of 33 cm, the visual
angle of one pixel will be 300 sec-of-arc.
For
this commonly used NTU300 printed on 6x4 inch photos,
to be precise, test distance of 33 cm would give a stereopsis of exactly 300
sec-of-arc.
During
the IBM PC era, Dr. Ji-Hau Jan (deceased) recommended using QuickBASIC
4.0, and later QuickBASIC 4.5, to create NTU
stereograms. He wrote many subroutines to help speed up program execution and
developed various other computer tools for ophthalmic use.
Dr.
Luke Lin once hoped I could create a 150” stereogram. Given the resolution
limits, as calculated earlier, a stereogram on a 6x4 inch photo needs to be
tested at a distance of 66 cm (33 x 2 cm) to achieve a
150” stereopsis. Test distance of 66 cm seems too long and not very convenient
for clinical use.
Small
angle esotropia would potentially pass the contour stereograms like Titmus, but can never pass the random-dot stereopsis test of
300”. We thus think random-dot stereogram is much more
sufficient for visual screening than contour stereograms.
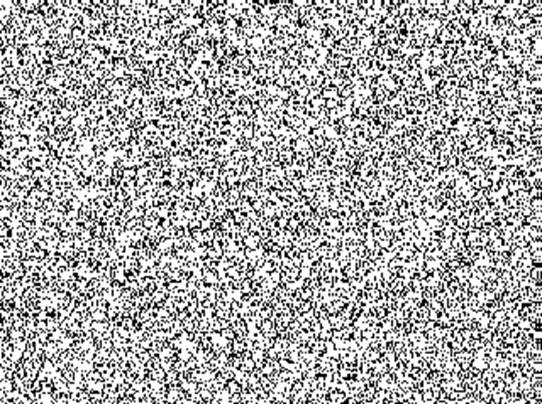
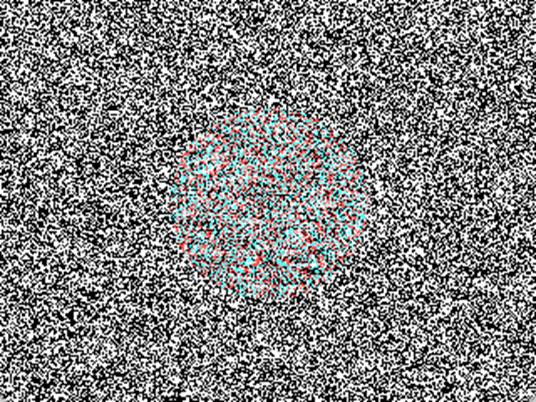
The
early computers limited our use of more pixels, which could be seen as a
fortunate constraint. If too many pixels were used, the random-dot stereogram
might become difficult to read. The left image shows the 320x240 pixels, 50%
density random-dot pattern used in NTU300, while the right image shows a
random-dot pattern of 1280x960 pixels. An excessively high resolution makes the
texture of the random-dot pattern less distinct, resulting in a blurry
appearance. With fewer texture available for the two
eyes to fuse, the information needed to disclose the disparity is also reduced,
making the stereogram harder to read.

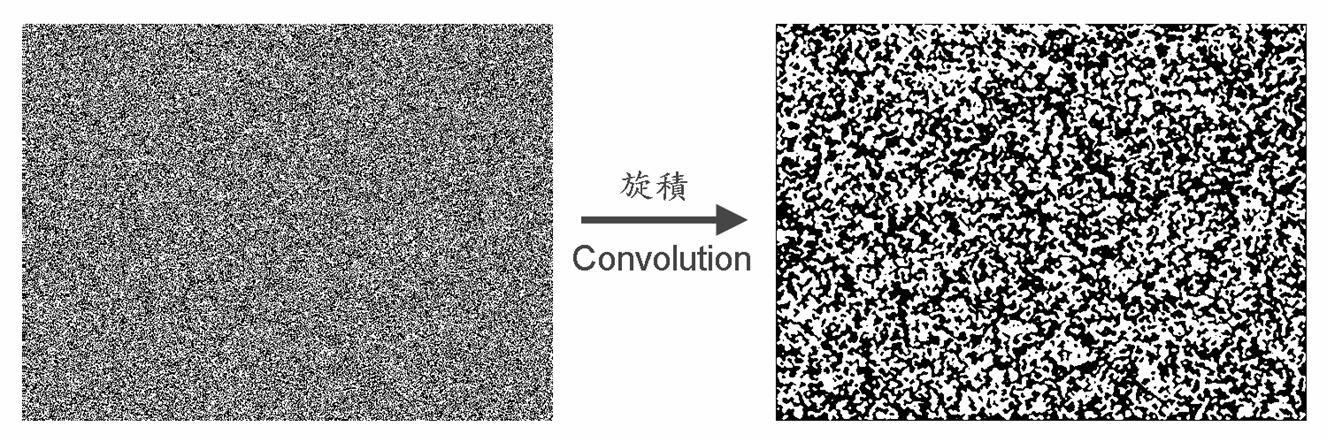
If
we want to use high resolution random-dot patterns to achieve finer stereopsis,
we need to remove the high spatial frequency components (details) in each
half-stereogram. We convolve digitally the half-stereogram several times to
remove high spatial frequency while keeping the low spatial frequency
components, to facilitate the fusion between two eyes.
Convolution
should be performed as the final step in creating a stereogram. If convolution
is performed earlier than the logical operations, monocular cues will appear
that defies the very nature of random-dot stereograms. Dr. Shao-Ming
Yan(deceased) of the Beijing Naval Hospital in mainland China created a new
version of a random-dot stereograms (left). You’ll find monocular cues of the
hidden figure they tried to bury within the stereogram (right).
The
figures embedded in the random-dot stereogram are essentially monochromatic.
The left and right half-stereograms are composed of black and white dots. To
separate the right and left eye, the white and black dots of the right
half-stereogram are overlaid with blue and black color, to be seen by the right
eye wearing blue lens; the white and black dots of the left half-stereogram are
overlaid with red and black color, to be seen by the left eye wearing red lens.
This type of binocular dissociation using red and blue or red and green colors
is called anaglyph.
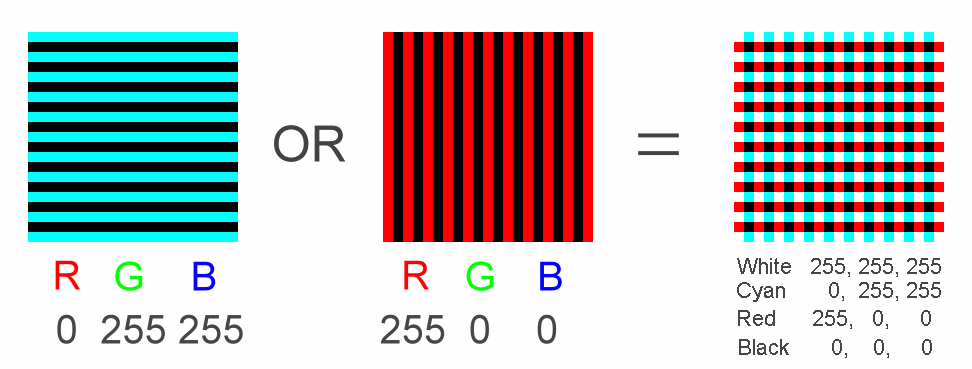
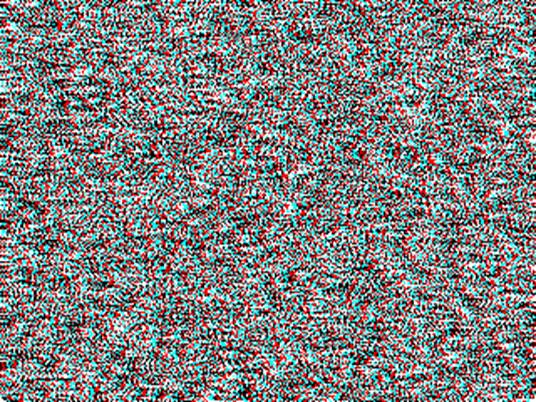
TNO
uses red and green for binocular dissociation. We have tried red and green, to
find that the effect is not as good as red and blue (actually, cyan)
dissociation. Computer colors are composed of red, green, and blue (R, G, B).
Each color has 256 levels of intensity (0-255). Red-green dissociation uses red
(255, 0, 0) and green (0, 255, 0), while red-blue dissociation uses red (255,
0, 0) and blue (0, 255, 255). The left figure shows red-green dissociation, and
the right figure shows red-blue dissociation.


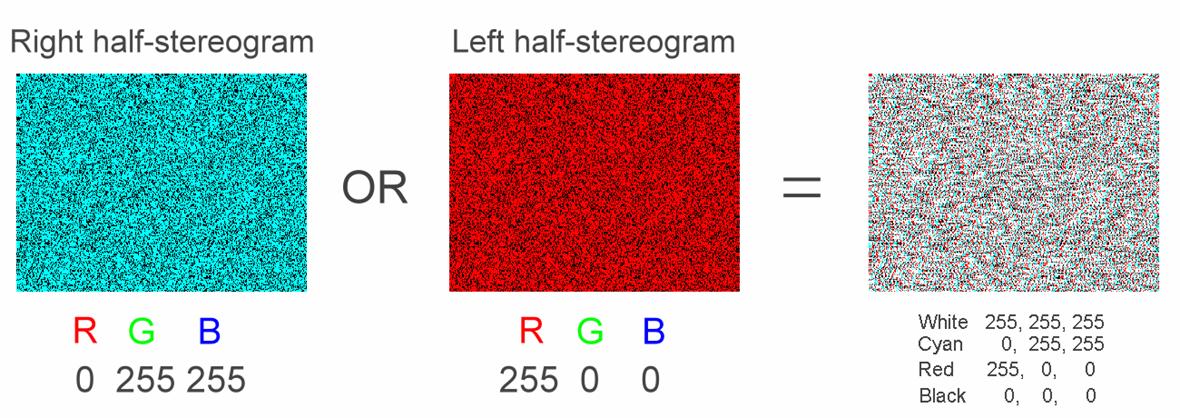
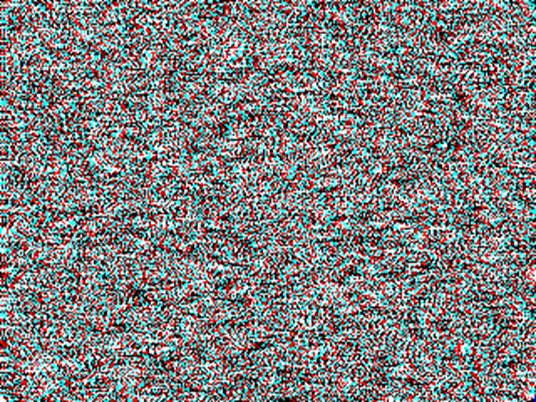
The
right half-stereogram is overlaid with cyan, and the left half-stereogram is
overlaid with red. The two half-stereograms are superimposed together with
logical OR operation. The pixels of the combined figure have four colors:
white, cyan, red and black (see figure).
The
background of two half-stereograms should also be slightly spaced apart.
Otherwise, the identical texture of the left and right backgrounds will be
completely overlapped, resulting in only black and white dots, and the hidden
figure will be revealed as monocular cue (left figure). Our experience suggests
a minimum of three or four dots apart are needed to avoid this monocular cue.
Similarly, the embedded figures of two half-stereograms should not be too close
together, otherwise the monocular cue will be revealed (right figure).


Depth
= 5 pixels = (+5 pixels) – (0 pixels) Depth
= 4 pixels = (0 pixels) – (-4 pixels)
Initially,
I shifted the right half-stereogram two points to the left and the left
half-stereogram two points to the right. This crossed
backgrounds looks floating above the real paper plane, and the embedded
figure goes even higher above the paper plane. The two eyes need to converge
more to fuse, making it more difficult for people of weaker convergence to read
(left image). The current version shifts the right half-stereogram
two points to the right and the left half-stereogram two points to the left. It
requires less convergence to fuse, and thus easier to read. After fusion, the
background appears to recess back, lower than the real paper plane (right
image).


Depth
= 2 pixels = (+6 pixels) – (+4 pixels) Depth
= 2 pixels = (-2 pixels) – (-4 pixels)
In
addition to the six pairs of stereograms of 480", 240", 120",
60", 30", and 15" for detailed quantification of stereopsis, the
TNO Stereotest has three 33 min-of-arc (1980 sec-of-arc) stereograms for
learning and screening.
The
NTU300 is of one pixel disparity. We tried to mimic TNO 33 min-of-arc in our
NTU stereograms. The closest one is 7 pixels disparity,
of stereopsis of 300x7 = 2100 sec-of-arc = 35 min-of-arc. We abbreviate it as
NTU35, or more precisely, NTU35’, or NTU2100”.
Viewing
an NTU 300 sec-of-arc stereogram (NTU300”), the figure appears 1 pixel above
the background (relative height), and the background is 4 pixels below the
paper plane (absolute height). Therefore, the figure is 3 pixels below the
paper plane (absolute height). We write this as Depth = 1 pixel = (-3 pixels) –
(-4 pixels). Most people simply feel the figure comes above the background, but
if they observe carefully the relative depth of the figure to the surface of
the paper, they will discover that the figure is actually
below the surface. About the 35 min-of-arc NTU stereogram (NTU35' or
NTU2100"), the figure rises 7 pixels above the background (relative
height). While the background is 4 pixels below the paper plane (absolute
height), the figure is 3 pixels above the paper plane (absolute height). We
write this as Depth = 7 pixels = (3 pixels) – (-4 pixels). Most people will just notice that the figure rises significantly above
the background, much higher than that of NTU300. However, if they observe carefully
the relative depth to the paper plane, they will find that the figure is above
the paper plane, while the background is below the paper plane.
Based
on the method described in https://ahwang.url.tw/WebArticles/Creating%20RDS%20step-by-step-English.htm,
we created and share four interesting random-dot stereograms below:


Logo of Universal Eye Center Depth 1 pixel = (-3 pixels) – (-4 pixels)


Arthur Jampolsky (AJ) 100th birthday Depth 7 pixels = (+3
pixels) – (-4 pixels)
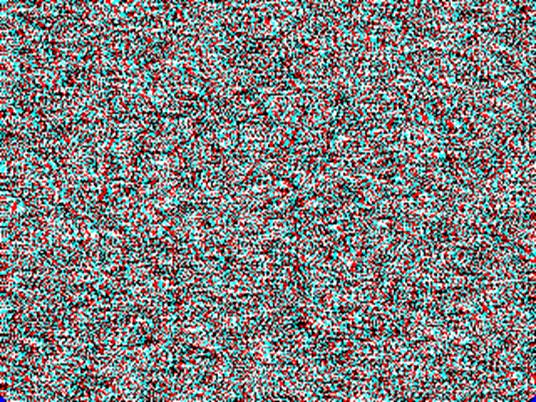


‘Eye’ in Chinese Depth
7 pixels = (+3 pixels) – (-4 pixels)
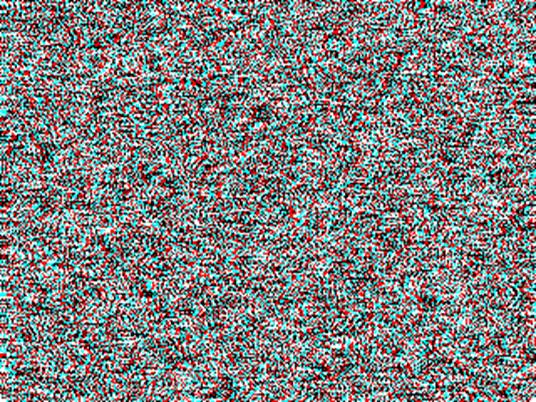


Checkerboard Depth
7 pixels = (+3 pixels) – (-4 pixels)
We
initially took pictures of the computer screen, laminating the photographs into
five cards, front and back (left figure). Later, with the development of
digital photo processing, we printed photos directly from the computer files.
We worked with the Kodak store to adjust the CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow,
Key/Black) color palette, and the color and clarity of NTU300 were
significantly improved (right figure).


Dr.
Luke Lin referenced the name of TMC color vision test book from Tokyo Medical
College and named our random-dot stereograms NTU (National Taiwan University)
random-dot stereopsis test (NTU RDS). Luke screened preschoolers and
schoolchildren with NTU RDS of 300 sec-of-arc disparity, hence the familiar
‘NTU300’.
TNO
is a random-dot stereotest produced by Netherlands. It includes three 33'
(=1980") stereograms for learning and screening, and six pairs for
quantitative test. The quantitative stereograms are of 480", 240",
120", 60", 30", and 15".
If
we would like to create a 15 sec-of-arc stereogram like TNO on a 6x4-inch
photo, meaning the visual angle of each pixel must be as small as 15
sec-of-arc, how many pixels are needed at a testing distance of 40 cm? The
calculation is as follows:
6
x 2.54 / n / 40 x 180/pi x 60 x 60 = 15" à n =
5239 pixels
In
other words, a 6x4-inch photo would require 5239 x 3493 pixels to produce a 15
sec-of-arc stereogram. For comparison, NTU's resolution is only 320x240 pixels!
We haven't even attempted such a high resolution yet. A 6-inch width contains
5239 pixels, close to 900 dpi (dots per inch). It requires a high-end printer
to achieve that. Think that it has already been published and sold by
Netherlands in the 1970~80s!s
Stereopsis
testing, like visual acuity testing, measures spatial resolution, both measured
in visual angles.
Visual
acuity that can resolve 1 min-of-arc is considered Snellen 1.0; visual acuity
that can only resolve 2 min-of-arc is considered Snellen 0.5. "NTU
300" means there’s a disparity of 300 sec-of-arc, or 5 min-of-arc, between
the half-stereograms of the two eyes; "NTU 35" means there's a 35
min-of-arc, or 2100 sec-of-arc disparity, between the half-stereograms of the
two eyes.
During
clinical testing, if a patient can't see the embedded shape, we ask him/her to
move forward to see if they can get it. Just like if they can't answer on
visual acuity testing, they might get it by moving forward. The increased
visual angle at nearer distance allows them to see it.
The
note "NTU300(+) at 20 cm" in the medical record means that the
patient can only resolve the 300 sec-of-arc stereogram
of regular test distance of 33 cm when they move forward to 20 cm. His/her
stereopsis is thus 300 x 33 / 20 = 495 seconds. Clinical testing doesn't
necessarily require such precise numbers. This test result tell
us that this patient's stereopsis is worse than 300 sec-of-arc, but it’s not
too bad to require the NTU 35 min-of-arc testing. During subsequent follow-up
visits, if he/she can pass the NTU300 at 35-40 cm, it indicates his/her
stereopsis has improved.
Creating
NTU stereograms was part of my doctoral dissertation, which involved comparing
the stereopsis threshold of NTU300 and TNO stereotest.
Patients
with normal stereopsis or complete stereopsis blind, that is, those who passed
TNO 60 sec-of-arc and those who failed TNO 33 min-of-arc, could not be used to
verify the threshold.
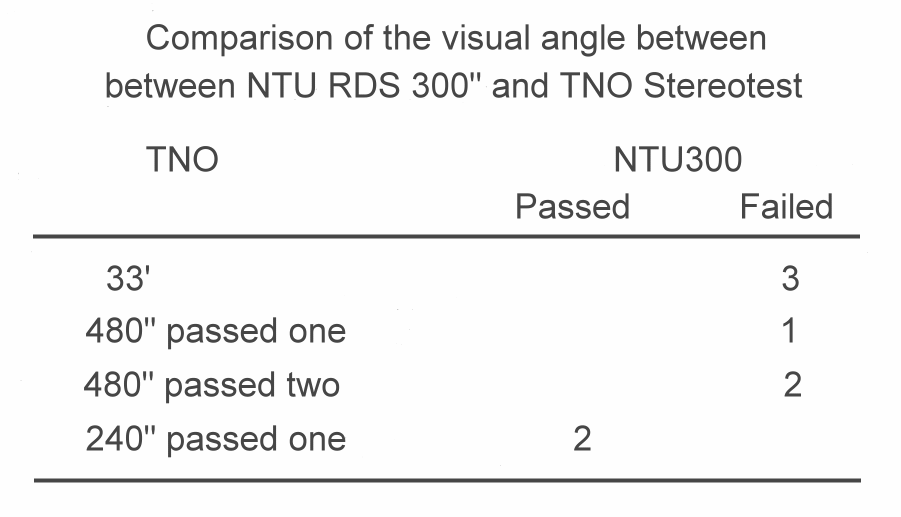
We
identified a small number of patients with moderate stereopsis, whose
stereopsis are not perfect [TNO 60(-)] nor stereopsis blind [TNO 33(-)]. The
comparison showed an exact match between the stereopsis threshold of NTU300 and
TNO stereotest: 6 patients who passed TNO 33 min-of-arc or TNO 480 sec-of-arc
but failed TNO 240 sec-of-arc also failed NTU 300 sec-of-arc; 2 patients who
passed TNO 240 sec-of-arc but failed TNO 120 sec-of-arc also passed NTU 300
sec-of-arc (see the table).
Dr.
Luke Lin implemented the "Precursor Program to Promote Visual Screening
for Preschool Children in Taiwan" commissioned by Department of Health
(now Ministry of Health and Welfare) from 1990 to 1994, and recommended that visual screening include two
items: (1) distance vision and (2) NTU300.


Since
2000, Health Promotion Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare has been
implementing a comprehensive screening program for preschool children using (1)
distance vision and (2) NTU300. During this period, Dr. Shu-Mei Li once
questioned why NTU300 was used for stereopsis screening?
What authority does NTU300 have? Dr. Luke Lin then asked me to apply for a
patent for NTU300 (see figure).

A
few years later, the annual patent fee skyrocketed. Our patent wasn't
originally oriented toward profit, and at the time, National Taiwan University
didn't provide subsidy for patent maintenance, we therefore stopped to renew
the patent.
NTU300
screens primarily for small angle esotropia, anisometropia, and other forms of
unilateral amblyopia.
During
school visual screenings, children with amblyopia, unable to see the vision
chart with the worse eye, often remove the patch covering their good eye to
peek, and thus miss the screening (a false negative). But these children, with
a significant difference of the best corrected visual acuity between two eyes,
won’t be able to pass the NTU300 screening.
For
large angle esotropia, parents naturally would take their children to
ophthalmologist by themself, which is not included in the screening purpose.
If
pass the NTU300 test, we will reply on the school's
vision report "normal stereopsis". I personally think 300 sec-of-arc
is sufficient as normal stereopsis clinically.
TNO
stereotest has three 33" RDS’s for learning and screening. Besides that there are quantification tests of 480", 240",
120", 60", 30", and 15". Most people would pass 60", yet fail 30" and 15". With so many
steps, I don’t think it will give more clinical information than NTU300 test
alone.
In
outpatient examinations, the use of the NTU35’ (=2100") in addition to the
NTU300" is as following:
If
fail NTU 35", we will report "abnormal stereoscopic perception."
Two conditions which will pass NTU35' yet fail NTU300" are esophoria and
anisometropia, which are considered as “subnormal stereopsis”. We explain to
the parents that their child's stereopsis is not good enough,
but is not completely absent (there's room for improvement).
For
Hyperopia + ET the stereopsis may gradually return to normal after wearing
glasses.
X(T)
post-operatively may show some DVD and subnormal stereopsis, but hopefully it
will gradually improve to NTU300"(+).
National
Taiwan University Random-dot Stereogram (NTU RDS)
NTU300" NTU35'
(or NTU2100")
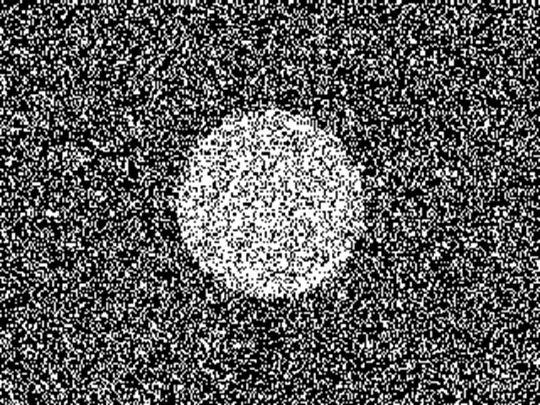
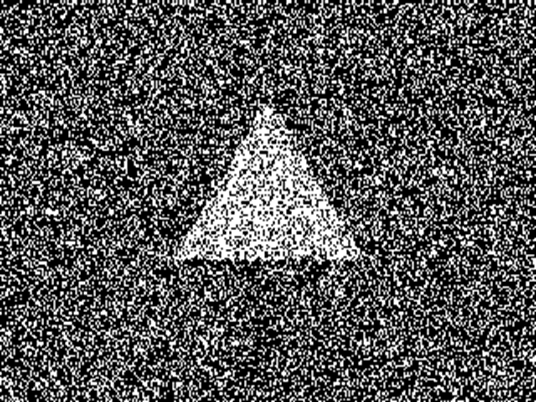
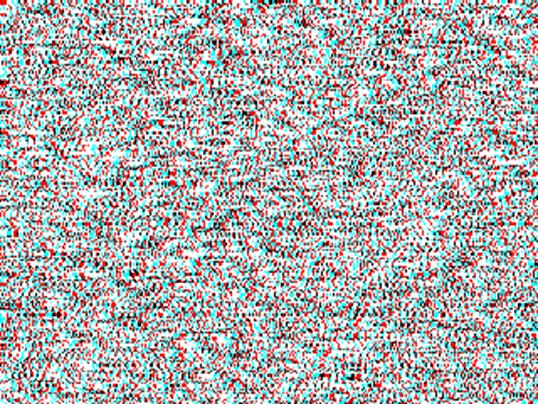
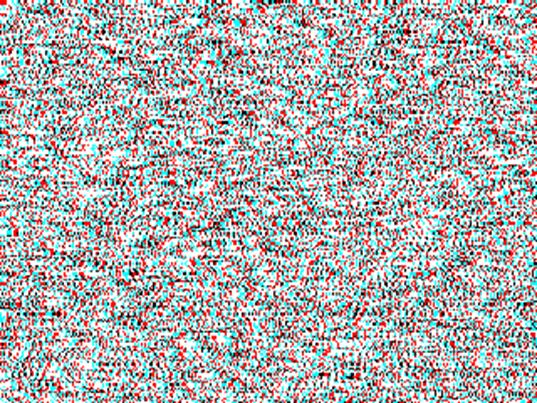


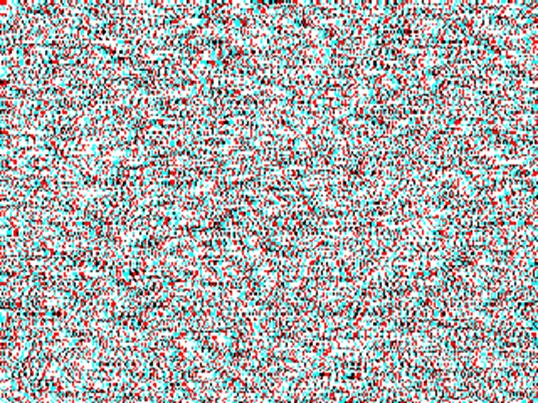
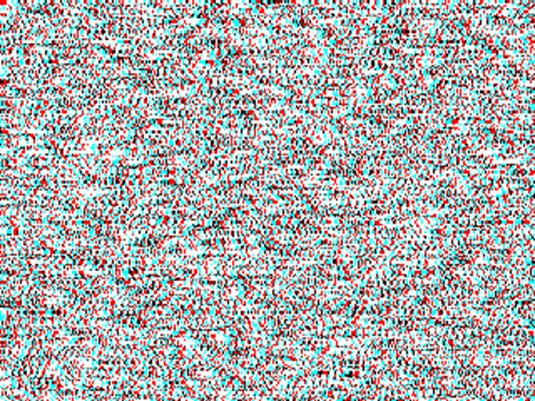



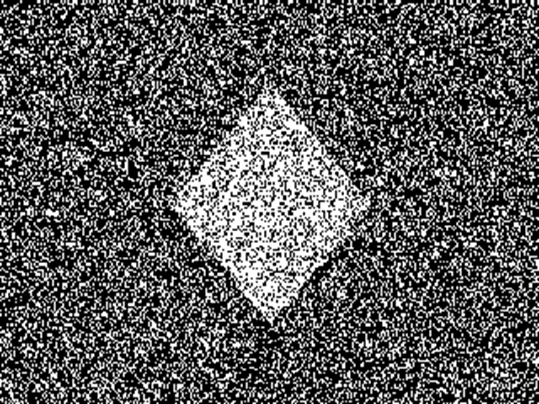

Left
side shows 300 second-of-arc, 1-pixel disparity NTU RDS (NTU300”) and the right
side shows 35 minute-of-arc, 7-pixels disparity NTU RDS (NTU35’) (or NTU2100”).
The
Computer division of Universal Eye Center expanded NTU RDS into a
cross-platform program, https://www.eyedoctor.com.tw/Stereopsis_Screening/,
which can be run on web browsers under various operating systems such as
Windows, iOS, Android, and macOS etc.
We
had once proposed that Health Promotion Administration (HPA), Ministry of
Health and Welfare switch to the computer version of NTU300 for visual
screenings for preschoolers and schoolchildren. First, the testing process is
more engaging; second, it eliminates the pollution concerns of the photo-based
NTU300. The HPA hopes to have medical schools/medical centers lead the effort,
and this idea has not been implemented yet.
Another
problem is the red-blue lens issue. Each brand of monitor uses different
phosphors, and some screen colors don't match perfectly the color of red-blue
lenses.
I
designed this grid pattern to checkout that. The grid should appear as
horizontal stripes through blue lens and vertical stripes through red lens.
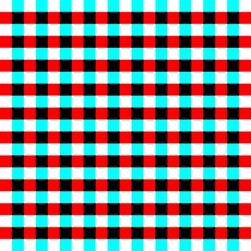
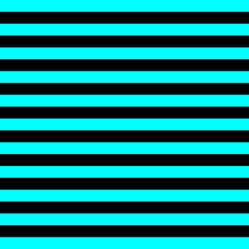

The
less ghost image the better. The less ghost image it will be easier to read the
red-blue dissociated anaglyphs on the screen.
Usually,
blue lens is fine, but red lens is harder to get rid of the ghost image.
I
currently use an Acer monitor, and the red and blue lenses do a very good job
of separating the left and right eye images.
This
is a 3' x 6', 2mm thick sheet of acrylic, cut into 5x5cm red and blue lenses
and stick them together. The colors are adequate for anaglyph viewing.
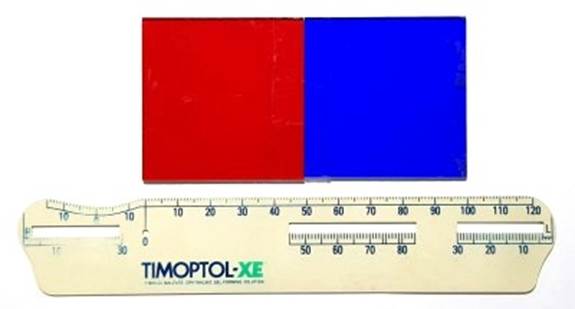
One
idea is to distribute this nice red-blue acrylic lens to everyone in need. You
can hold it directly in front of your eyes to see the anaglyph, or you can take
it apart and ask the optician to cut the acrylic lenses to fit them onto the
glasses frame.

If
you're taking the NTU300 screening online, another option for red-blue glasses
is to purchase on Shopee. Please note: the right eye is blue lens
and the left eye is red lens.
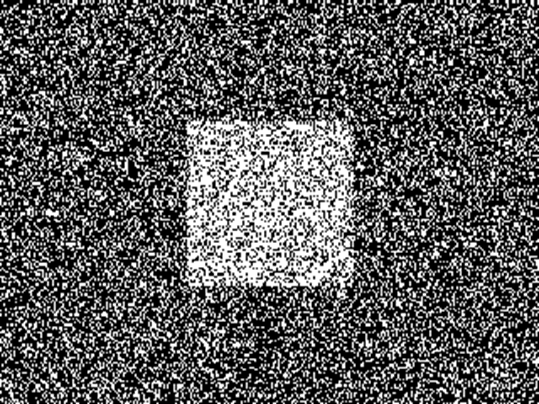
To
test the NTU300"/NTU35" please also print a card or photo for the
preverbal children (ages 2.5 to 3.5) to select with their hands the shape they
see (see the picture). The NTU300”/NTU35’ can typically be tested two or three
months earlier than the E chart of visual acuity test.
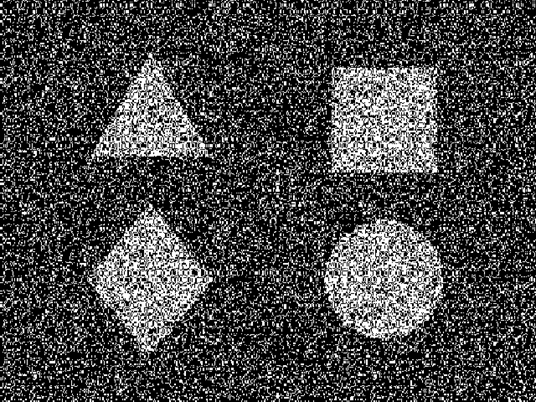
When
testing NTU clinically, after answering two or three questions correctly, I
like to cover the patient's left eye with a patch and ask, "Can't you see
the triangle with your right eye?" Then, I cover the right eye and ask,
"Can't you see the triangle with your left eye either?... You only have
two eyes, so if you can't see the triangle with either eye, where does the
triangle come from?" Keep covering the right eye,
then switch to the next stereopsis question and ask, "You can't answer
that, right?"
Use
this program to explain that stereopsis is a kind of binocular vision and
cannot be seen with one eye only. At the same time, observe whether the child
is curious about not being able to see shapes with either eye, and whether they have a scientific traits.
Compared
to the card version of NTU, testing NTU on computer screen allows you to
perform the patch test described above, making it much more fun.
Please
try https://www.eyedoctor.com.tw/Stereopsis_Screening/.
The applause and cheers at the end suggest that children undergoing the
screening will be eager to try it out after watching their classmates taking
the test, and the test will be completed quickly and joyfully. (I haven't actually tested it myself. Can anyone help me test it and
report back?)
After
testing stereopsis, we explain to parents: "Even if both eyes have 1.0
vision, they won't pass the stereopsis test if they have esotropia or
cross-eyes."
"We
depict visual function simply with three parameters: the visual acuity of each
eye, and the stereopsis of the two eyes working together."
The
computer division of Universal Eye Center has developed a cross-platform
program for stereopsis testing. Besides static stereopsis tests of NTU300” and
NTU35’ there are programs for motion stereopsis (Binocular Depth-from-Motion,
BDFM) tests.
Stereopsis
test – https://www.eyedoctor.com.tw/Stereopsis/
Stereopsis
screening – https://www.eyedoctor.com.tw/Stereopsis_Screening/
